This tutorial illustrates how to install MySQL server on a CORE9G25 Board with 256 MBytes of RAM
To install MySQL Server don't use a minicom session on the debug port but an SSH session over LAN.
Install mysql-server package from the Debian repository by typing:
~# apt-get update ... ~# apt-get install mysql-server
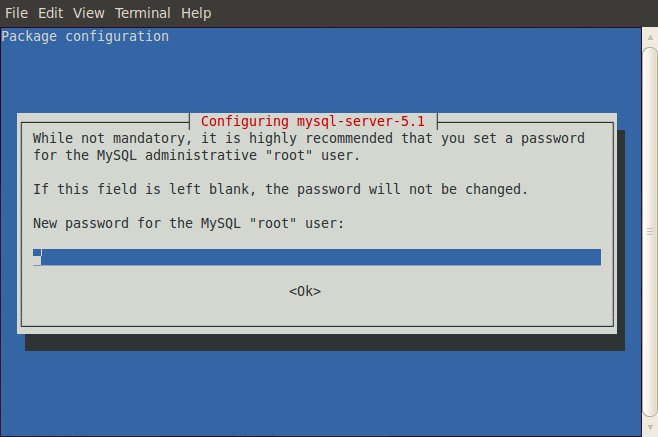
The installation script will ask you the password to use to access as root user to the MySQL server. It is very important to remember this password to have access to the MySQL DB.
When installation is finished check whether mysqld daemon is already running by typing:
~# ps ax | grep mysql 3393 ? S 0:00 /bin/sh /usr/bin/mysqld_safe 3504 ? Sl 0:09 /usr/sbin/mysqld --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --user=.... 3505 ? S 0:00 logger -t mysqld -p daemon.error 3650 pts/0 S+ 0:00 grep mysql ~#
Create a dummy database called for example mydb using the mysqladmin utility:
~# mysqladmin -u root -p create mydb Enter password:
Use the SQL queries saved on the following file to create an example table called addressbook.
addressbook.sql: This code example is downloadable from the CD://Debian/playground/python/mysql/addressbook.sql
/*DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `addressbook`;*/ CREATE TABLE `addressbook` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, `phone` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `website` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1; LOCK TABLES `addressbook` WRITE; INSERT INTO `addressbook` VALUES (1,'CORE9G25 Systems srl','+39 (06) 99-12-187','www.CORE9G25systems.it'), (2,'Atmel Corporate','+1 (408) 441-0311','www.atmel.com'), (3,'Digikey','+1 (800) 344-4539','www.digikey.com'); UNLOCK TABLES;
Using the mysql client utility fill the mydb database by typing:
~# mysql mydb -u root -p < addressbook.sql Enter password:
Now run the mysql command line utility to check the table and contents just created:
~# mysql -u root -p Enter password: Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 42 Server version: 5.1.66-0+squeeze1 (Debian) Copyright (c) 2000, 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql>
Select the mydb database just created:
mysql> use mydb
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
and make a SQL query to see the contents:
mysql> SELECT * FROM addressbook; +----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+ | id | name | phone | website | +----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+ | 1 | CORE9G25 Systems srl | +39 (06) 99-12-187 | www.CORE9G25systems.it | | 2 | Atmel Corporate | +1 (408) 441-0311 | www.atmel.com | | 3 | Digikey | +1 (800) 344-4539 | www.digikey.com | +----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Insert a new record:
mysql> INSERT INTO addressbook (name,phone,website) VALUES ('Mouser','+39 02 575 065 71','www.mouser.com');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.10 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM addressbook;
+----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| id | name | phone | website |
+----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+
| 1 | CORE9G25 Systems srl | +39 (06) 99-12-187 | www.CORE9G25systems.it |
| 2 | Atmel Corporate | +1 (408) 441-0311 | www.atmel.com |
| 3 | Digikey | +1 (800) 344-4539 | www.digikey.com |
| 4 | Mouser | +39 02 575 065 71 | www.mouser.com |
+----+------------------+--------------------+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
#
Move the MySQL data dir
By default MySQL save the data in /var/lib/mysql. To move this data for example on /media/data/mysql stop the MySQL server.
~# /etc/init.d/mysql stop Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld.
Create the new directory:
~# mkdir /media/data/mysql
Copy over the database folders:
~# cp -R /var/lib/mysql /media/data/mysql
Edit the /etc/mysql/my.cnf lines:
#datadir = /var/lib/mysql datadir = /media/data/mysql
Update the directory permissions:
~# chown -R mysql:mysql /media/data/mysql
Start MySQL again:
~# /etc/init.d/mysql start Starting MySQL database server: mysqld . .. Checking for corrupt, not cleanly closed and upgrade needing tables..
Access MySQL Server remotely over SSH
For security reasons the MySQL TCP/IP default port 3306 is only open to local connections.
If you want to access your MySQL database remotely from a client located on another device you could use two ways:
- Open the port 3306 to external connection. This way is useful to get access from GUI native interfaces available on Linux, Windows, iOS or Android.
- Create a port-forwarding through an SSH tunnel. This method is usable on Linux systems.
Open the port 3306 to external connection
Edit the /etc/mysql/my.conf file. Find this line:
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
the comment out it placing a # character at beginning line:
#bind-address = 127.0.0.1
Restart mysql by typing:
# /etc/init.d/mysql restart Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld. Starting MySQL database server: mysqld . . . .. Checking for tables which need an upgrade, are corrupt or were not closed cleanly..
Now we have to grant access to this our db:
# mysql -uroot -p mysql> GRANT ALL ON mydb.* TO remote_user_name@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'remote_user_password'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> quit
Port-forwarding through an SSH tunnel
In this way your MySQL client application thinks it's connecting to a local MySQL server, but it's really connecting to the remote MySQL server through the SSH tunnel.
Let's try with the Python example:
addrlist.py: This code example is downloadable from the CD://Debian/playground/python/mysql/addrlist.py
import MySQLdb
db=MySQLdb.connect(host="127.0.0.1",port=3306,db="mydb",user="root",passwd="CORE9G25")
cur = db.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM addressbook;")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
print row
Type on a Linux PC this command:
$ ssh -L 3306:localhost:3306 root@CORE9G25_board_ip
The syntax is:
ssh -L localport:hostname:remoteport username@servername
If you already have MySQL running on your local machine then you can use a different local port for the port-forwarding, and just set your client tools to access MySQL on a different port.
Now run on your PC addrlist.py:
~# python addrlist.py (1L, 'CORE9G25 Systems srl', '+39 (06) 99-12-187', 'www.CORE9G25systems.it') (2L, 'Atmel Corporate', '+1 (408) 441-0311', 'www.atmel.com') (3L, 'Digikey', '+1 (800) 344-4539', 'www.digikey.com')
Related links
Documentation Terms of Use
The Acme Systems srl provides this Debian system development and user manual.
The origin of these doc came from the website: http://www.acmesystems.it
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.